Understanding Turbocharged Engines: Power, Performance, and Why They Matter
Table of Contents
Toggle
In the world of modern automotive engineering, turbocharged engines have become a staple in performance vehicles, passenger cars, and even commercial trucks. These engines offer a balance of power and efficiency that naturally aspirated engines often struggle to match. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what turbocharged engines are, how they work, their advantages and drawbacks, and why they are a popular choice among tuners and racing enthusiasts.
What Is a Turbocharged Engine?
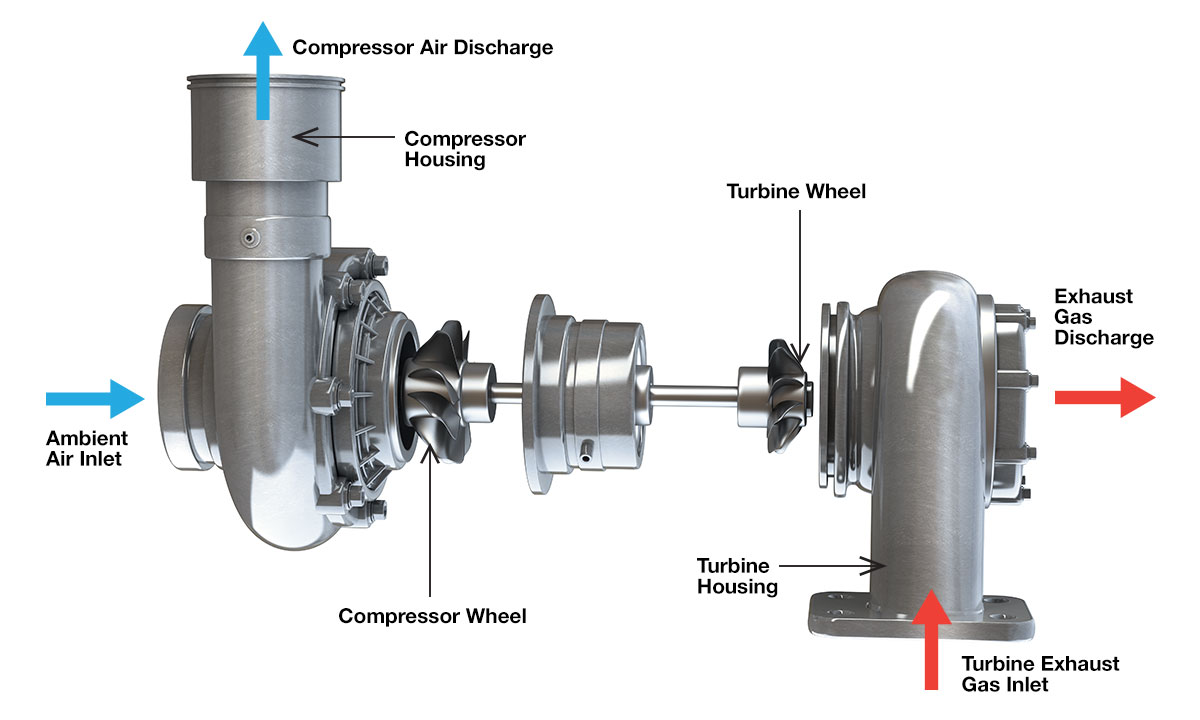
A turbocharged engine uses a turbine-driven forced induction system to increase an engine’s efficiency and power output by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber. This allows the engine to burn more fuel and produce more power than it could otherwise.
Unlike naturally aspirated engines, which rely on atmospheric pressure, turbocharged engines compress the intake air using a turbocharger. The turbocharger itself is powered by exhaust gases, making use of otherwise wasted energy.
Common turbocharged engine models we offer:
-
Volkswagen 2.0 TDI (CBAA, CFFB, CJCA)
-
Ford 2.0 EcoBoost (JN5G, HNDA)
-
Audi 1.8 TFSI (CDAA, CDHB)
-
BMW N20 2.0L Turbocharged
-
Mercedes-Benz OM651 2.1 CDI
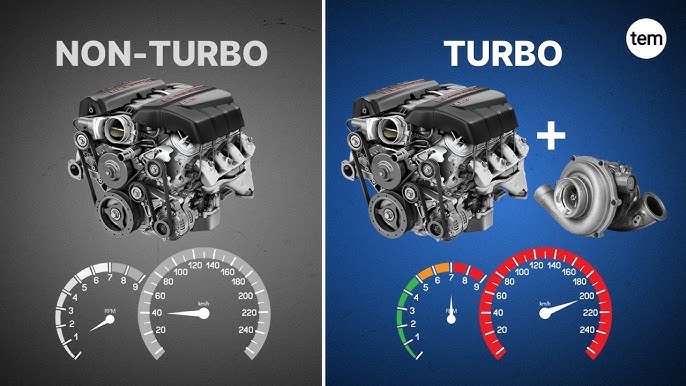
Turbocharged vs. Naturally Aspirated Engines
| Feature | Turbocharged Engines | Naturally Aspirated Engines |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Higher for the same displacement | Limited by atmospheric air intake |
| Fuel Efficiency | More efficient under optimal conditions | Less efficient at high-performance levels |
| Engine Size | Can be smaller and lighter | Often requires larger displacement |
| Maintenance | More complex, higher repair costs | Simpler and usually cheaper to maintain |
| Throttle Response | Turbo lag may be present | Immediate throttle response |
Naturally aspirated engines tend to have smoother, more linear power delivery, which some drivers prefer. However, for most modern driving scenarios and especially for performance applications, turbocharged engines offer a more practical solution.
Why Turbocharged Engines Are Popular Among Tuners
For automotive enthusiasts and tuners, turbocharged engines are highly desirable due to their upgradability. A stock turbocharged engine can often be tuned to provide 20–50% more horsepower with just software updates and supporting modifications like an upgraded intercooler or exhaust system.
Common turbocharged engines used for tuning:
-
Volkswagen EA888 (CZDA, CHHB) – Highly popular among GTI and Golf R tuners.
-
Ford EcoBoost 3.5L V6 – Found in vehicles like the Ford F-150 and Raptor.
-
Audi 2.0 TFSI (CHH, CAEB) – Known for responsiveness and mod potential.

Turbocharging in Motorsports and Racing Applications
In motorsports, turbocharged engines are prized for their power-to-weight advantage. A smaller turbocharged engine can produce as much power as a much larger naturally aspirated one, making it ideal for applications where weight and space are concerns.
For example:
-
BMW N54 and N55 turbo engines are widely used in amateur and professional drift cars.
-
Mitsubishi 4G63T and Subaru EJ20/EJ25 Turbo engines dominate rally scenes.
-
Audi’s 2.5 TFSI (DAZA) has become a popular base for drag builds.
When selecting a turbo engine for performance or motorsports use, customers often consider:
-
Turbo lag and how quickly the turbo spools.
-
Cooling systems (especially intercoolers).
-
Fuel quality and engine mapping.
-
Aftermarket part availability.
Real-World Benefits for Everyday Drivers
Turbocharged engines aren’t just for racers. Many daily-use vehicles now come equipped with turbochargers to meet stricter emissions standards without compromising performance. For example, a 1.5L turbocharged engine may perform on par with an older 2.4L naturally aspirated one while offering better fuel economy.
These are perfect for:
-
Small SUVs like the Ford Escape 1.5 EcoBoost
-
Compact sedans such as the Hyundai Elantra 1.6T
-
Crossovers like the Chevrolet Equinox 2.0T
Things to Watch Out For
While turbocharged engines offer many benefits, they also require careful maintenance:
-
Use high-quality synthetic oil to handle higher operating temperatures.
-
Let the turbo cool before turning off the engine after hard driving.
-
Monitor boost levels if the vehicle is modified or tuned.
Conclusion
Whether you’re looking to enhance performance, boost efficiency, or dive into the world of motorsports, turbocharged engines offer a compelling blend of advantages. At [Your Company], we stock a wide variety of turbocharged engines including models like CBAA, CDAA, OM651, and N20 — ready for both replacement and performance applications.
Contact us today to learn more or check our product catalog to find your next engine upgrade.